Table of Contents >> Show >> Hide
Finding the center of a circle is a common task in geometry, whether you’re working with physical circles for drawing or determining the center of a circle in a more mathematical setting. Knowing how to find the center can help you with various tasks, such as creating accurate designs, solving geometric problems, or even determining key points for navigation and plotting. In this article, we will explore four effective methods to find the center of a circle, each suited to different scenarios and skill levels. Let’s dive in!
Method 1: Using the Perpendicular Bisector
The most widely used method for finding the center of a circle involves using its diameter. The perpendicular bisector method is ideal when you have a circle drawn on a piece of paper and a straightedge at your disposal. Here’s how you do it:
- Draw the Diameter: First, draw a straight line through the circle. This line must pass through the edge of the circle on opposite sides. This is your diameter.
- Find the Midpoint: Next, measure or estimate the midpoint of the diameter. The midpoint is the middle point along the line.
- Draw the Perpendicular Line: Using a protractor or right-angle tool, draw a perpendicular line from the midpoint of the diameter. This line should cross through the center of the circle.
- Center of the Circle: The point where the perpendicular line intersects the circle’s edge is the center of the circle.
This method is effective and straightforward for physical drawings and offers a high degree of accuracy if done carefully. It can also be applied to digital designs using various drawing software programs.
Method 2: Using the Compass
If you have access to a compass, finding the center of a circle becomes even easier. A compass allows you to measure the radius of the circle accurately and can be used to construct additional geometric shapes that help identify the center. Follow these steps:
- Place the Compass at Any Point on the Circle: Open your compass to the radius size of the circle and place the point of the compass on any point along the circumference of the circle.
- Draw a Circle of Smaller Radius: With the compass point fixed, draw a small arc that intersects the original circle at two points.
- Repeat the Process: Without changing the radius, repeat the process from a different point along the circumference.
- Locate the Intersection: The point where the two arcs intersect is the center of the circle.
This method is often used in classroom settings or for creating precise geometric constructions. A compass ensures that the construction is symmetrical, which makes it a reliable way to locate the center of a circle.
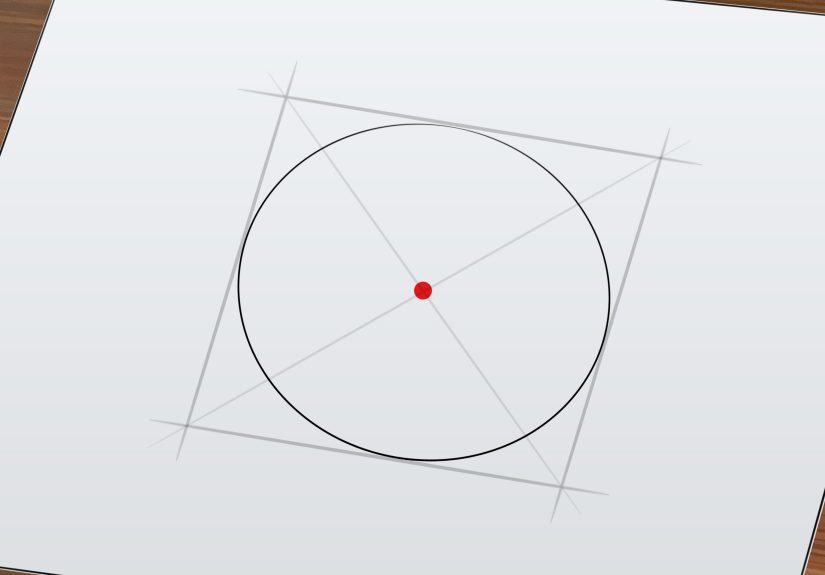
Method 3: Using Tracing Paper and the Intersection of Chords
If you’re working with a physical circle, such as one drawn on paper or found in a diagram, and you don’t have a compass or ruler, tracing paper can serve as a simple yet effective tool to find the center. Here’s how to do it:
- Trace the Circle: Lay a sheet of tracing paper over the circle and carefully trace the circumference with a pencil or pen.
- Draw Two Chords: Draw two different chords of the circle. A chord is any straight line that connects two points on the circumference but does not necessarily pass through the center.
- Find the Midpoints of the Chords: Measure and find the midpoints of both chords. Mark these midpoints.
- Draw Perpendicular Bisectors: Use a ruler to draw a perpendicular line from each midpoint of the chords.
- Locate the Center: The point where the two perpendicular bisectors intersect is the center of the circle.
This method works well for quick and simple tasks when precision tools like compasses or rulers are unavailable. It requires basic knowledge of geometry, but it’s incredibly effective for finding the center with minimal equipment.
Method 4: Using the Circle’s Equation (For Advanced Users)
If you’re working with a circle defined by its equation in a coordinate plane, you can find the center using algebra. A circle’s general equation is:
(x – h)² + (y – k)² = r²
In this equation, (h, k) represents the coordinates of the center, and r is the radius. Here’s how you can find the center:
- Identify the Equation: Ensure you have the correct equation of the circle, which will be in the standard form as shown above.
- Extract the Center Coordinates: The center of the circle will be at the point (h, k). These values are simply the numbers you subtract from x and y in the equation.
- Confirm the Center: Once you’ve identified (h, k), verify by checking that this point satisfies the circle’s equation when substituted back.
This method is perfect for those dealing with circles in mathematical problems, such as in calculus or coordinate geometry, where the circle is represented by an equation.
Conclusion
In summary, finding the center of a circle can be done through a variety of methods, ranging from practical physical tools like compasses and tracing paper to more mathematical approaches involving algebra. Whether you’re using a straightedge and compass or solving equations in a coordinate plane, these methods all have their own advantages depending on the situation. Mastering these techniques will not only enhance your geometry skills but also provide you with tools to solve real-world problems that involve circles, from design to engineering.
Additional Insights: Practical Experience in Finding Circle Centers
Finding the center of a circle isn’t just a classroom skillit’s something that comes in handy in various real-world scenarios. Whether you’re designing a logo, laying out a floor plan, or even constructing something as fundamental as a round table, knowing how to locate the center of a circle is a foundational skill. I’ve used these methods in various DIY projects, from woodworking to graphic design, where accuracy is key. One memorable experience was when I had to lay out a circular pattern for a garden pathway. Using the perpendicular bisector method allowed me to create a perfectly centered design, which, in turn, made the entire project come together beautifully.
Another memorable instance was during a digital art project, where I needed to design a circular logo. Using a digital compass tool (essentially the same concept as the physical compass) in design software made it easy to find the center and ensure all elements were symmetrically placed. These types of projects are where geometric accuracy can make all the difference, whether you’re crafting a decorative piece or solving complex mathematical problems.
In summary, while the methods discussed are traditional, they’re still incredibly relevant today. Whether you’re doing something as simple as drawing a circle with a compass or applying advanced algebra in a coordinate plane, the core principle remains the same: finding that central point is crucial for symmetry, accuracy, and clarity in your designs and solutions.