Table of Contents >> Show >> Hide
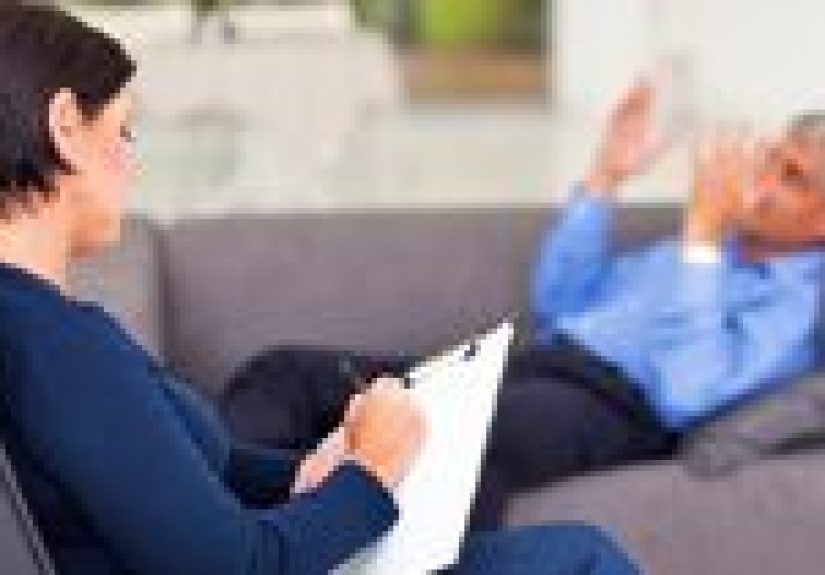
Depression can be a crippling mental health condition, affecting millions of people worldwide. While there are many ways to treat depression, one therapeutic approach stands out for its emphasis on the individual’s role in the healing process: Client-Centered Therapy (CCT), also known as Person-Centered Therapy (PCT). Developed by Carl Rogers, this approach emphasizes the therapeutic relationship, empathy, and active listening, all of which are crucial in helping individuals navigate their emotional struggles. In this article, we’ll explore how Client-Centered Therapy works, its benefits for treating depression, and why it’s a preferred method for many seeking relief from their mental health challenges.
What is Client-Centered Therapy?
Client-Centered Therapy (CCT) is a form of psychotherapy that was developed by Carl Rogers in the 1940s. The approach is grounded in the belief that individuals possess an innate ability to understand and resolve their issues when provided with the right conditions. Unlike more directive forms of therapy, where the therapist leads the conversation and gives advice, CCT is non-directive. In this model, the therapist’s primary role is to create a safe, supportive environment in which the client feels comfortable exploring their thoughts and feelings at their own pace.
Key to this approach is the belief that people are inherently good and have the ability to self-actualizemeaning they can achieve their fullest potential. CCT is based on three core principles:
- Unconditional Positive Regard: The therapist offers acceptance and support without judgment, creating a space where the client feels valued and understood.
- Empathy: The therapist works to deeply understand the client’s experience and emotions, reflecting back these feelings to ensure the client feels heard and validated.
- Congruence: The therapist is authentic and transparent in their interactions, ensuring that their actions align with their feelings and beliefs.
These principles are designed to foster a relationship in which clients feel empowered to explore their emotions and ultimately gain insight into the root causes of their depression. Rather than simply prescribing solutions, CCT encourages clients to find their own answers, leading to long-term emotional growth and healing.
How Does Client-Centered Therapy Help with Depression?
Depression often stems from a variety of sources, including past trauma, negative self-beliefs, and societal pressures. Traditional therapies might focus on addressing the symptoms, but Client-Centered Therapy takes a deeper, more holistic approach by addressing the underlying emotional pain. Here’s how CCT can be particularly helpful for those struggling with depression:
1. Building Trust and a Safe Space
For many people with depression, the ability to trust others can be a significant challenge. Feelings of shame, guilt, and unworthiness often accompany the condition, making it difficult to open up. Through the therapist’s unconditional positive regard, clients are reassured that their feelings are valid and that they are worthy of care. This safe, non-judgmental space allows individuals to explore their emotions freely without the fear of being criticized or misunderstood.
2. Fostering Self-Awareness
Depression can often cloud a person’s ability to see their own strengths and abilities. CCT encourages self-exploration, which can help individuals recognize their own emotional needs, desires, and resources. By providing empathy and reflecting the client’s thoughts and feelings, the therapist helps the person see themselves from a more compassionate perspective, leading to improved self-awareness and self-esteem.
3. Empowering the Client
One of the core tenets of Client-Centered Therapy is that the client is the expert on their own life. This is particularly empowering for individuals with depression, who may feel overwhelmed or powerless in other areas of their life. By fostering a sense of autonomy, CCT helps individuals gain the confidence to make decisions that support their emotional well-being, ultimately promoting long-term healing and resilience.
4. Enhancing Emotional Regulation
People with depression often struggle with managing their emotions. CCT’s focus on empathy and validation allows individuals to process and release pent-up feelings in a healthy way. As clients feel more understood and accepted, they are better able to express their emotions without fear of rejection, leading to improved emotional regulation and a reduction in depressive symptoms.
5. Strengthening the Therapeutic Relationship
The therapeutic relationship in Client-Centered Therapy is built on trust, respect, and mutual understanding. This relationship becomes an important tool in the healing process, as the client learns how to form and maintain healthier connections with others. For individuals with depression, this aspect of therapy can be especially beneficial, as it teaches them how to navigate their relationships with a new sense of self-worth and confidence.
Why Choose Client-Centered Therapy for Depression?
While there are various therapeutic approaches to treating depression, Client-Centered Therapy stands out for its focus on empathy, self-exploration, and empowerment. Here are some reasons why CCT may be the right choice for someone dealing with depression:
- Non-judgmental and compassionate environment: The therapist’s ability to listen with empathy without judgment allows the client to feel safe and understood, which is essential for emotional healing.
- Focus on the individual: CCT places the client at the center of the therapeutic process, allowing them to take ownership of their journey toward healing and self-discovery.
- Long-term results: By fostering self-awareness and emotional regulation, CCT promotes lasting emotional growth, helping individuals manage depression and improve their overall well-being.
- Highly personalized: The therapy is tailored to the client’s specific needs, ensuring that the approach resonates with the individual and addresses their unique experiences.
Challenges and Limitations of Client-Centered Therapy
While Client-Centered Therapy is highly effective for many people, it may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with severe or chronic depression. Since it is a non-directive approach, some clients may struggle with the lack of structure or guidance, particularly if they are used to more directive therapies. Additionally, individuals with severe depression may require a combination of therapies, such as medication and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), to address their condition effectively.
Combining CCT with Other Therapies
In some cases, combining Client-Centered Therapy with other therapeutic approaches can provide more comprehensive treatment. For example, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) may be used alongside CCT to help clients challenge negative thought patterns and develop coping strategies. Medication may also be prescribed in more severe cases of depression to manage symptoms while the client works through their emotional issues in therapy.
Experiences with Client-Centered Therapy for Depression
Many individuals who have undergone Client-Centered Therapy for depression report significant improvements in their emotional well-being and overall outlook on life. For example, one client shared that after several sessions with a CCT therapist, they felt less isolated and more empowered to confront their depressive thoughts. The therapeutic relationship provided a safe space where they could express their feelings of sadness, guilt, and hopelessness without fear of judgment. Through this process, they began to develop a more compassionate view of themselves, which led to lasting improvements in their mental health.
Another individual shared their experience of feeling stuck and overwhelmed by their depression, unable to see a way out. After beginning Client-Centered Therapy, they found that their therapist’s empathy and validation helped them process their emotions at their own pace. This gentle approach allowed them to reflect on their experiences and gain insights into the underlying causes of their depression. Over time, they felt more confident in their ability to manage their emotions and make decisions that supported their mental well-being.
These stories highlight the power of the therapeutic relationship in Client-Centered Therapy. While the process may take time, individuals often report feeling heard, understood, and validated, which helps them heal from depression in a way that is both personal and lasting.
Conclusion
Client-Centered Therapy offers a compassionate and empowering approach to treating depression, placing the individual at the center of their healing process. By fostering a non-judgmental, empathetic environment and promoting self-awareness, CCT helps individuals manage their emotions, build trust, and develop the confidence to confront their challenges head-on. While it may not be the right choice for everyone, CCT has proven to be a highly effective treatment for many individuals struggling with depression. With its emphasis on personal growth, self-compassion, and emotional healing, Client-Centered Therapy is a powerful tool for those seeking lasting change in their mental health journey.
sapo: Client-Centered Therapy offers a compassionate approach to treating depression, focusing on empathy and self-exploration to help individuals heal. Learn how it works and why it’s effective.